A solid grasp of mathematical formulas is crucial for success in math. This Quick Reference Guide to Basic Math Formulas brings together essential formulas from key topics such as algebra, geometry, and trigonometry, providing students with a practical tool for quick learning and effective revision. Whether you’re preparing for exams, tackling homework, or building long-term math skills, this guide is designed to support your studies every step of the way.
Algebra
Linear Equation of two variables ; ax + by + c=0
Quadratic Equation = ax2+ bx + c = 0
Quadratic Formula=
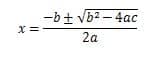
Discriminant = D = b2 – 4ac
- D > 0 means two real roots
- D = 0 means one real root
- D < 0 means two complex roots
Binomial Expansion

(a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
(a – b)2 = a2 – 2ab + b2
(a+b)3=a3+3a2b+3ab2+b3
a2 – b2 = (a – b)(a + b)
a2+b2 = (a+b)2 – 2ab
a2+ b2 = (a-b)2 + 2ab
Geometry
Area of Triangle = 1/2 * base * height
Area of Circle =π *D2/4 = π*r2
Circumference of Circle = 2*π*r = π*D
Area of Square = side2
Parameter of a square = 4*side
Area of Rectangle = Length * width
Parameter of a Rectangle = 2*(Length + width)
Area of Trapezoid =(widthtop+ widthbottom)*height/2
Volume of Cylinder =π*r2*L
Volume of Cone =π*r2*h/3
Volume of Sphere = 4*π*r3/3
Surface Area of Sphere= 4*π*r2
Pythagorean Theorem
- Hypotenuse2= perpendicular2 +Base2
Distance Formula

Mid Point Formula

Trigonometry
- Sin(θ) = Opposite/Hypotenuse = Perpendicular / Hypotenuse
- Cos(θ) = Adjacent/Hypotenuse= Base / Hypotenuse
- Tan(θ) = Opposite/Adjacent = Perpendicular / Base
- Cosec(θ) = 1 / sin(θ)
- Sec(θ) = 1 / cos(θ)
- Cot (θ) = 1/ tan(θ)
- Tan(θ) =sin(θ)/cos(θ)
- Pythagorean Identity
- sin2(θ) + cos2(θ) = 1
- tan2(θ) + 1 = sec2(θ)
- 1+ cot2(θ) =cosec2(θ)
- Law of Sines =a/sin(A) = b/sin(B) = c/sin(C)
- Law of Cosines
- c2 = a2 + b2– 2*a*b*cos(C)
- b2 = a2 + c2– 2*a*c*cos(B)
- a2 = b2 + c2– 2*b*c*cos(A)
- Half Angle Formula
- sin2(θ/2) = [1- cos(θ) ] / 2
- cos2(θ/2) = [1+ cos(θ) ] / 2
- Double Angle Formula
- sin(2θ) = 2*sin(θ)*cos(θ)
- cos(2θ) = cos2(θ)-sin2(θ)
- Sine Addition/Subtraction Formula
- Sin (A + B) = sin (A)* cos (B) + cos (A)*sin(B)
- Sin (A – B) = sin (A)* cos (B) + cos (A)*sin(B)
- Cosine Addition/subtraction formula
- Cos (A + B) = cos (A)*cos (B) – sin (A) sin (B)
- Cos (A – B) = cos (A)*cos (B) sin (A) sin (B)
Statistics
Mean (Average)
- Mean of ungrouped data = (Sum of all observations) / (Number of observations)
- Mean of grouped data = Σ(f * x) / Σf, here; f is the frequency of each class and x is the midpoint of each class interval
Median
Ungrouped Data
Arrange the data from smallest to largest and count the data points(n), If total data points (n) is an odd figures, the median is (n+1)/2 term.and If there’s an even number of data points, the median is the average of the values of n/2 term and [(n/2) + 1 ]term.
Grouped Data
Median = l + ((n/2 – F) / f) * h
here:
l: Lower limit of the median class (the class containing the median)
n: Total number of data points
F: Cumulative frequency of the class preceding the median class
f: Frequency of the median class
h: Class interval width
Sequences and Series
- General Term of Arithmetic Sequence = an = a1 + (n – 1)*d
- General Term of Geometric Series = an= a1 * r(n-1)
- Sum of Arithmetic Series = Sn = n/2 * [2*a +(n-1)*d]
- Sum of Geometric Series =Sn = a * (1- rn )/( 1-r) (for r>1)

Leave a Reply